Research
Exosome characterization by Coffee ring effect: Size separation in evaporating droplet
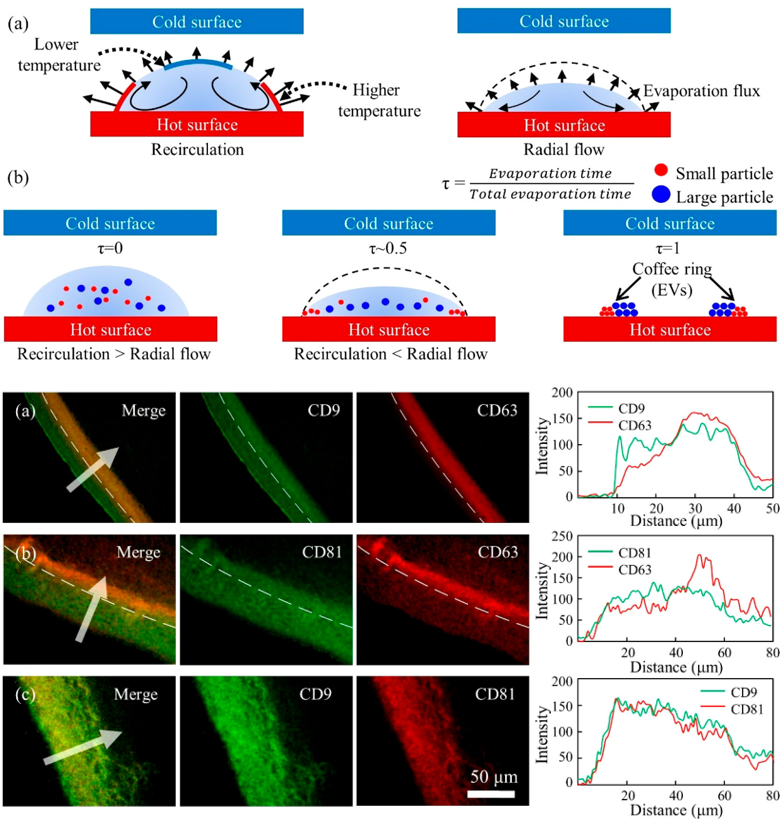
We introduce size separation that exploits Marangoni flow and the coffee-ring effect in microdroplets in which extracellular vesicles are spatially deposited at different location according to size of extracellular vesicle. Interestingly, the analysis of tetraspanin proteins of the extracellular vesicles facilitated by this method reveals that the size of extracellular vesicles is correlated with expression of tetraspanin proteins (CD9, CD63, CD81) that are associated with the size of extracellular vesicles.
- Reference
- Analysis of Extracellular Vesicles Using Coffee Ring, ACS Applied materials & interfaces, 2018
Exosome characterization by TIRF: optical microscopy system design
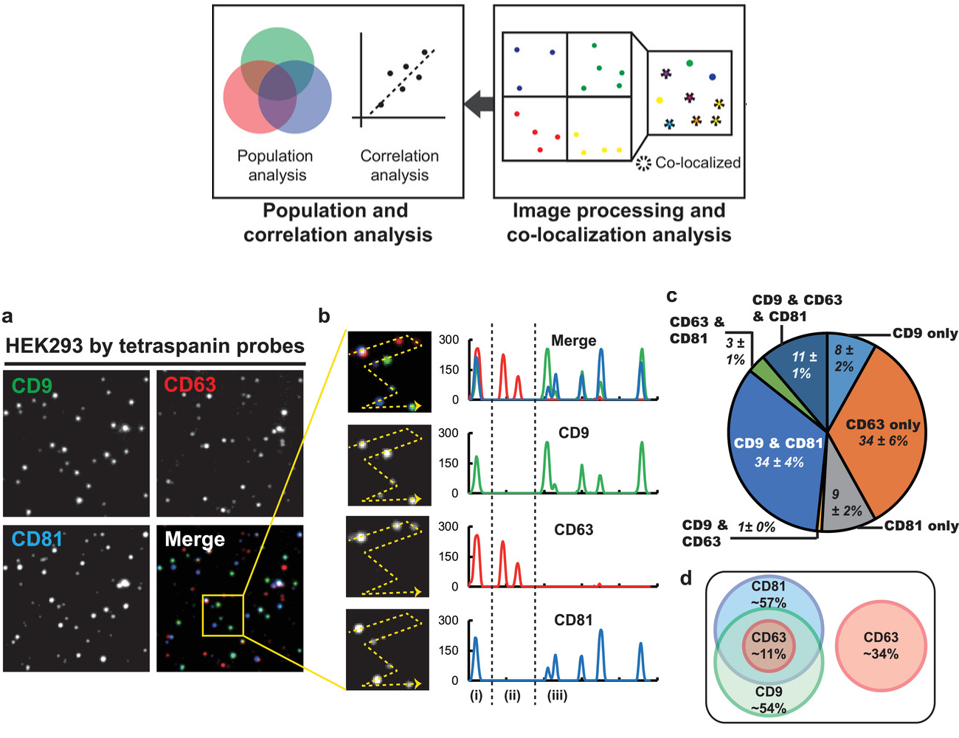
Optical microscopy technology using fluorescence has a lot of influence on the observation of the micro-world of micro-nano size, and is still used to observe many biological phenomena. In our research team, various optical systems have been developed to measure exosomes labeled with fluorescent proteins, and studies are underway to analyze the properties of exosomes by analyzing physical and chemical phenomena of nanoparticles.
- Reference
- Single‐vesicle imaging and co‐localization analysis for tetraspanin profiling of individual extracellular vesicles, Journal of Extracellular Vesicles, 2021
Single Extracellular Vesicle Analysis by NTA
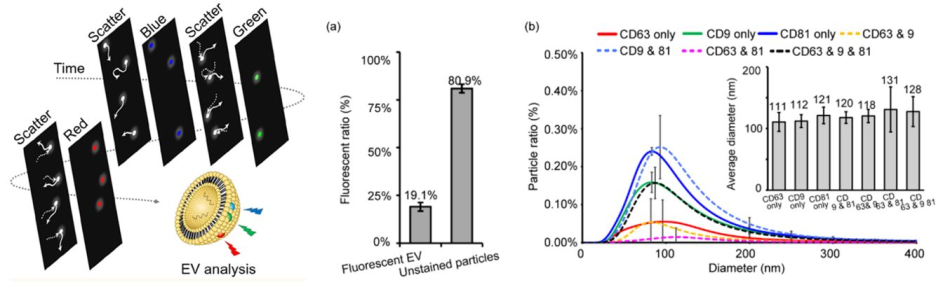
We demonstrate a fluorescence-based nanoparticle tracking analysis (NTA) system for the characterization of both the size and membrane protein expression of individual extracellular vesicles (EVs).
- Reference
- “Multifluorescence Single Extracellular Vesicle Analysis by Time-Sequential Illumination and Tracking”, ACS Nano, 2021